Simulation-Based Emergency Training for Athletic Trainers: Preparing for Critical Sports Medicine Events
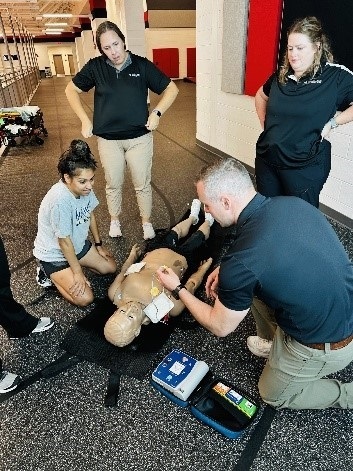
In July, the Center for Simulation and Innovation, in collaboration with Trauma Services, conducted a comprehensive emergency response training session for Northeast Georgia Health System (NGHS) athletic trainers. This high-impact educational initiative addressed the unique challenges athletic trainers face when managing life-threatening emergencies in sports environments, where immediate intervention can mean the difference between life and death. The training focused on four critical competency areas: Basic Life Support (BLS), Stop the Bleed hemorrhage control, anaphylactic shock management, and spinal precautions with patient transport preparation. Each module was specifically tailored to realistic athletic scenarios, including sudden cardiac arrest during physical exertion, traumatic injuries resulting from player collisions or falls, severe allergic reactions to environmental triggers such as insect stings or food allergens, and spinal cord injuries commonly associated with contact sports.
The hands-on simulation-based approach reinforced rapid response protocols and enhanced critical decision-making skills essential for effective emergency management in athletic settings. By practicing these lifesaving interventions in controlled, realistic scenarios, athletic trainers developed the confidence and technical proficiency necessary to respond effectively when seconds matter most. This collaborative training model between simulation education and trauma services demonstrates the health system’s commitment to comprehensive emergency preparedness across all healthcare disciplines, ensuring that athletic trainers are equipped with current evidence-based practices and standardized protocols that can significantly improve patient outcomes during sports-related medical emergencies.
New PGY4 Psychiatry Simulation Elective Enhances Teaching and Leadership Skills
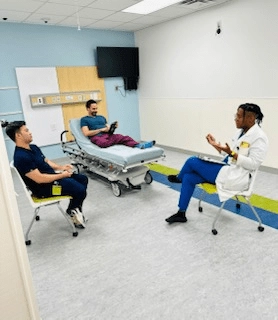
The Center for Simulation and Innovation and the Psychiatry Residency program have successfully launched an innovative PGY-4 psychiatry simulation elective with Dr. Otey as the first resident to participate in this groundbreaking rotation. This two-month intensive rotation is specifically designed to develop simulation education expertise while enhancing residents’ teaching and leadership capabilities through hands-on experience in scenario design, facilitation and debriefing methodologies. During this elective, participants gain valuable skills in educational best practices, PEARLS debriefing techniques and scholarly project development while contributing to our institution’s expanding simulation case library focused on mental health, interpersonal communication and cultural awareness scenarios. This elective provides residents with the opportunity to develop expertise in simulation-based education, which not only enhances their clinical and teaching skills but also positions them as future leaders in medical education and simulation training within the field of psychiatry.
Central Venous Catheter Workshop Series: A Structured Approach to Resident Education
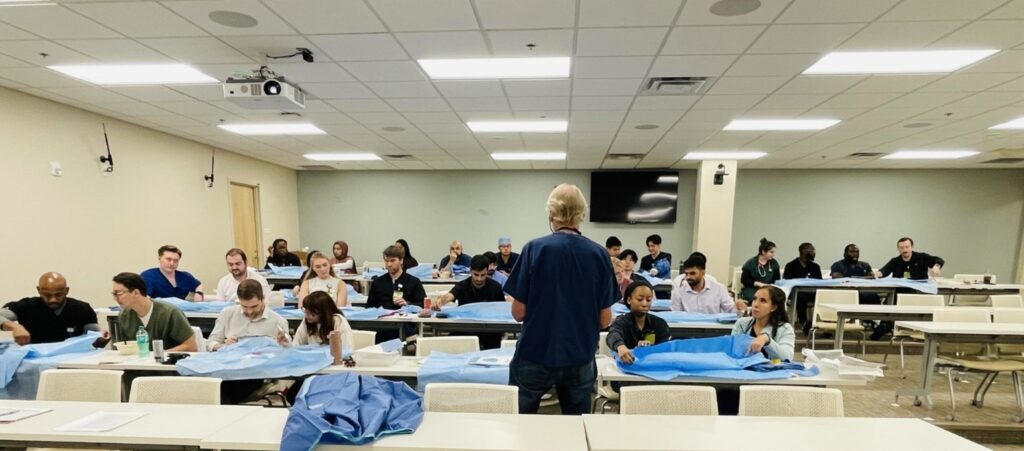

The Internal Medicine Residency program successfully implemented its second annual Central Venous Catheter (CVC) noon conference workshop series during July orientation, designed to reduce cognitive overload surrounding the complex multi-step process of central line placement. This three-part educational initiative strategically precedes formal procedure training with Dr. Hogue, which occurs during the first four Fridays of each month, ideally before residents’ initial ICU rotations. Workshop #1 focused on ultrasound-guided internal jugular vein cannulation, featuring instructional videos and hands-on practice with peer examination, task trainers, and vessel trainers under the mentorship of senior residents including PGY-2s, PGY-3s, and chief residents Dr. Velez and Dr. Majeed. Workshop #2, led by Dr. Hogue, concentrated on comprehensive kit contents review and sterile field preparation, while the final workshop will provide a complete video demonstration with expert commentary covering the entire insertion process, followed by an interactive Q&A session.
This structured approach addresses the cognitive complexity of central line insertion while maximizing limited training opportunities, allowing residents to enter their protected practice time with solid theoretical and practical foundations. The workshop series serves dual educational purposes by providing incoming PGY-1 residents with essential foundational knowledge while offering valuable skill reinforcement for upper-level residents. Through systematic preparation and multi-level mentorship, this innovative program enhances resident readiness for clinical practice and demonstrates the program’s commitment to comprehensive, safety-focused medical education that optimizes procedural competency development.
Cardiovascular Disease Fellows Begin Advanced Training with Simulation Lab Orientation
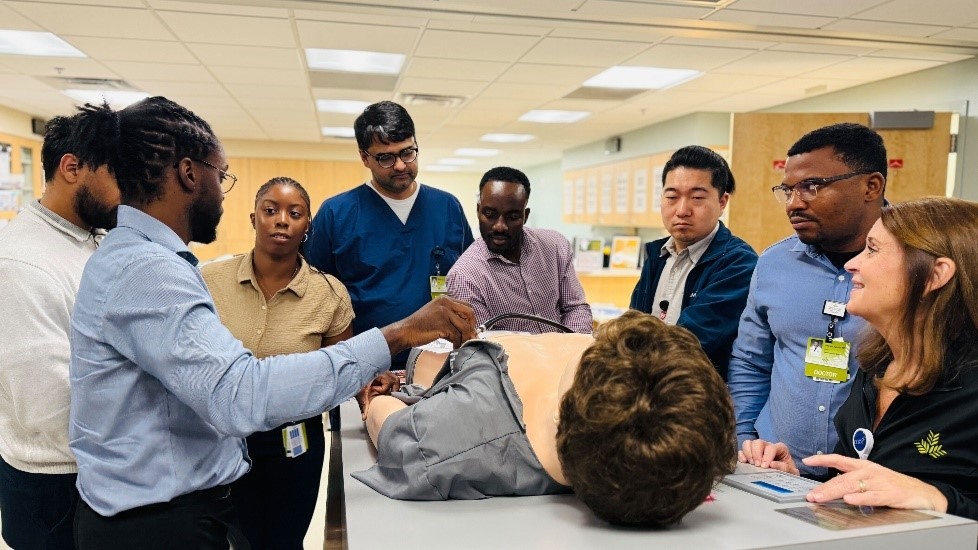
The incoming Cardiovascular Disease fellows received a comprehensive orientation to the GME Simulation Lab, marking the beginning of their hands-on training with cutting-edge medical technology. During the session, fellows were introduced to five specialized simulators designed to enhance their clinical skills across critical cardiology procedures. The Harvey simulator provided training on complex heart and lung sound identification, while the Vimedix system focused on advanced ultrasound techniques essential for cardiac imaging. Fellows also gained experience with the Pacer Man simulator for pacing issues and Swan-Ganz catheter placement and practiced lifesaving pericardiocentesis procedures for treating cardiac tamponade using dedicated simulation equipment. The orientation concluded with training on the Angio Mentor system, which provides realistic practice for both cardiac and vascular catheterization procedures. This comprehensive simulation-based approach ensures that the new fellows will develop proficiency in essential cardiology skills in a controlled, risk-free environment before treating patients.
General Surgery Residents Complete Intensive Skill-Based Orientation
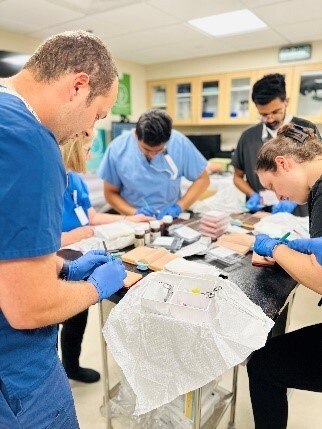
The General Surgery residency program recently completed an intensive two-day skill-based orientation for PGY-1 residents under the guidance of Dr. Foxhall, Dr. Strom and Dr. Butts. The simulation provided comprehensive hands-on training in critical procedural competencies essential for safe patient care. The rigorous curriculum covered fundamental procedures including central venous catheter placement, chest tube insertion, arterial line placement, advanced suturing methods, nasogastric tube insertion, Foley catheter insertion and IV access techniques, establishing a robust foundation in essential procedural skills before clinical rotations begin. Training extended beyond technical procedures to include specialized instruction in knot-tying methodologies, wound vacuum therapy, and debridement techniques, complemented by thorough radiology review sessions to enhance diagnostic interpretation capabilities. To develop collaborative skills crucial for operating room excellence, General Surgery residents participated in an innovative escape box team-building exercise designed to challenge problem-solving abilities and foster effective communication under pressure.
Comprehensive Pediatric Emergency Medicine Training Strengthens Resident Preparedness
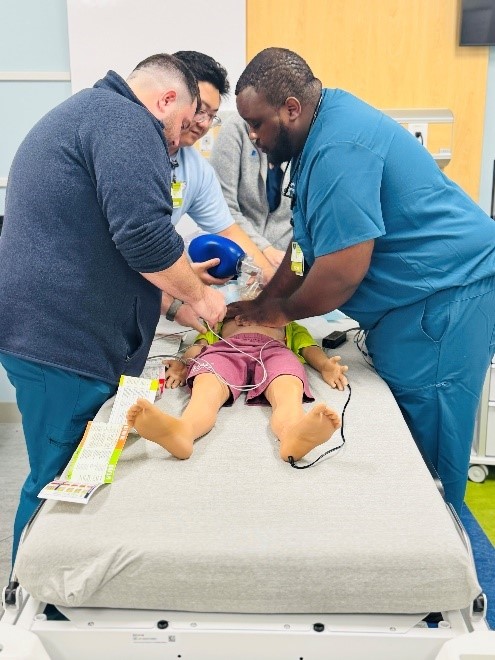
Emergency Medicine residents receive intensive pediatric training during their orientation phase to ensure they can confidently manage the unique challenges of treating young patients in emergency settings. Dr. Kelsey Craver, who holds dual board certifications in Emergency Medicine and Pediatric Emergency Medicine, recently led a comprehensive full-day training session that combined theoretical knowledge with hands-on practice. The educational program featured didactic lectures covering evidence-based approaches to pediatric seizures, neonatal and pediatric emergencies, and age-appropriate medication management.
The training emphasized procedural competency through high-fidelity simulations, including pediatric cardiac arrest scenarios, pediatric and neonatal intubation techniques, and supervised lumbar punctures. This integrated approach of expert instruction combined with simulation-based learning ensures residents develop both clinical knowledge and practical skills necessary to provide optimal care for pediatric patients, regardless of their intended subspecialty focus.
